
















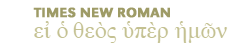
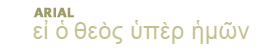

Nineveh, which was situated at the confluence of the Tigris and Khoser rivers (modern-day Mosul, Iraq), was first settled in the seventh millennium b.c. According to the Bible, Nimrod was the founder of the city (Gen. 10:11). Major excavations took place under the direction of Henry Layard from 1845 to 1854. The diagram pictures the results of those excavations, especially as they reflect the period of the Assyrian Empire (1420-609 b.c.). Around 1000 b.c. there occurred a great revival of Assyrian power, and Nineveh became a royal city. It was a thriving city during the first half of the first millennium, and contained such luxuries as public squares, parks, botanical gardens, and even a zoo. One of the great archaeological finds of the period is the library of King Ashurbanipal (669-627 b.c.; called Osnappar in Ezra 4:10). The size of the city was approximately 1,850 acres. The book of Jonah reflects the flourishing nature of Nineveh at this time (3:1-5). Nineveh eventually fell to the Medes and Babylonians in 612 b.c. The invading armies dammed the rivers that supplied water to the city, causing a flood that broke through one of the perimeter walls, giving the foreign armies access to the city.

The ESV Global Study Bible
Copyright © 2012 by Crossway.
All rights reserved.
Used by permission.
The Blue Letter Bible ministry and the BLB Institute hold to the historical, conservative Christian faith, which includes a firm belief in the inerrancy of Scripture. Since the text and audio content provided by BLB represent a range of evangelical traditions, all of the ideas and principles conveyed in the resource materials are not necessarily affirmed, in total, by this ministry.
Loading
Loading
| Interlinear |
| Bibles |
| Cross-Refs |
| Commentaries |
| Dictionaries |
| Miscellaneous |
